Barcode Fixed Mount Scanning: Functions, Applications and Benefits
This diagram shows the comprehensive applications and functions of fixed mount barcode scanning systems on production lines, mainly on conveyor belts. There scanners are of various technologies (CMOS, laser, imager and vision). Most scanners send data to host directly using a serial, ethernet or USB connection cables. Some scanners carry in their built-in circuits some intelligence boards to compare scanned numbers and images, and some models carry also input sensors (such as box presence sensor) and output triggers to trigger alarms or control some sorting system. The scanned output usually goes to a host system (PDA, control box, server) to store data (and possibly images) and to process additional more actions.
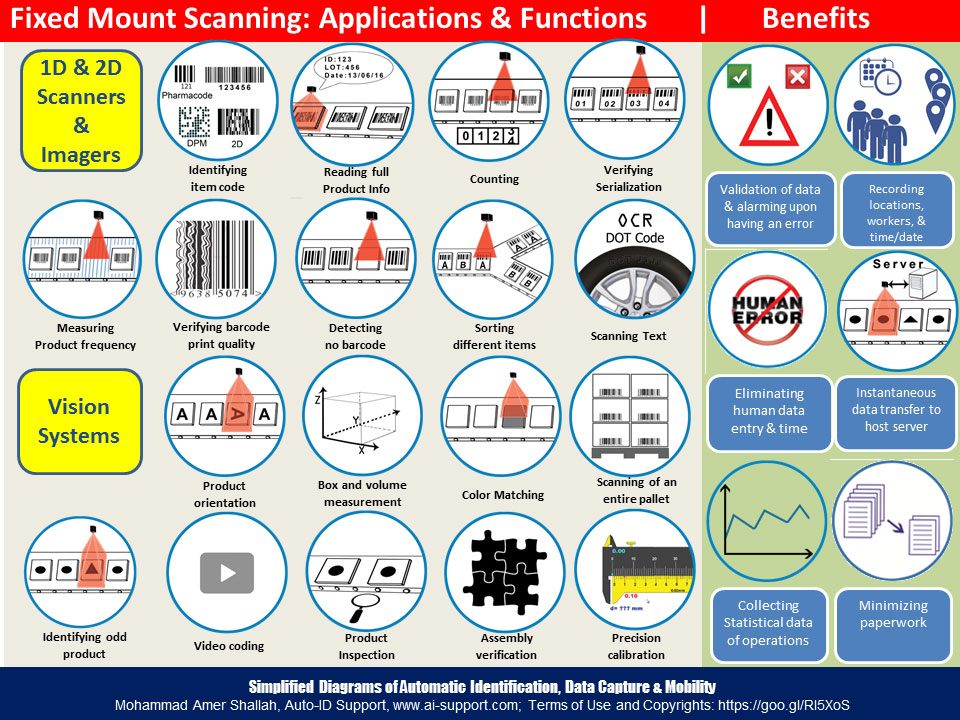
Here are the applications and functions:
1- Identification by barcodes: The is the basic function for identifying products by reading their barcodes.
- Counting: Reading consecutive boxes eventually leads to counting how many has passed.
- Sorting: If boxes with different items numbers are expected, reader can give signal to move box on another track. Additionally, if all boxes should be identical in certain batch production, any odd box will trigger a signal to remove the box away. This is commonly used in pharmaceutical industry to make sure all boxes and drug leaflets are the same and relevant to medicine in line.
- Verifying serialization: Scanners can monitor the sequence of numbers to make sure all items are going through their sequential numbers and nothing is missing, odd or misplaced.
- No-read detection: Scanners can be able to sense a box without a barcode. Action must be taken to ensure barcode existence (reprinting or reorienting the box to barcoded label side).
- Barcode quality verification: It is a rarely used application to verify that printed barcodes meet GS1 specification printing specifications.
- Product self-lookup: Scanners can read 2D codes that contain detailed encoded information about the product and can possibly alarm for certain parameter such as an expired date. Additional example is to print a label and apply it after scanning. Additionally, scanners can read from the barcodes the lot number (of a raw material) to save its data in production history.
- Reading text (OCR & Tyre dot codes): Advanced scanners are able to take fine images of an embossed rubber text on tyres and read them in the system to extract product information where usually it is hard to apply a labeled barcode.
- Product orientation: Some scanners can distinguish which side of the box is facing and thus might require reorientation.
- Image match verification: Some advanced scanners compare all the boxes to match all product side images so that they are the same 100%. This can be used in pharmaceutical industry to make sure printed instructions on boxes are all well printed and there is no missing character in the printing press.
- Reading barcodes of a full pallet at once: Any array of scanners can read all barcodes of all boxes on a pallet in a single moment and have batch data collectively gathered.
- Measuring volume & dimensions: Some specialized scanners have the ability to measure box dimensions and volume especially in the logistic industry.
- Image and video capturing: Special scanners can take shots of each box for quality control issues.
- Color Matching should all items should be the same
- Other advanced functions such as: assembly verification, contents verification, product inspection, and precision calibration
There could be much more applications depending on the requirements and this is limited by imagination. The flexibility lies in the ability to add sensors, relays and program host applications to gather data and make decisions.
Here are the common benefits:
a- Auto and/or online validation of captured data and alarming upon having an error
b- Data capture of site locations, production lines, operator names and date/time stamps
c- Reducing human data entry errors and time
d- Instantaneous data transfer to host server
e- Statistical analysis of info to make decisions, update instructions, knowing total operation time of each production line for maintenance issues
f- Minimizing paperwork
The diagram can help:
- AIDC manufacturers, specialists, distributors and integrators have a broad vision of what they are designing, developing, and selling and they see also how efficient their solutions would be.
- Software developers design their data capture applications in most efficient way to customers.
- AIDC resellers explain to their customers the benefits, the overriding of difficulties and cutting of costs.
Comments, suggestions, corrections, additions are welcome on this topic.
---
 About Amer Shallah
About Amer Shallah
I have been implementing automatic identification, data capture technologies, and mobility for 20 years in domains of business, government and security. The accumulated experience and continuous follow up on latest emerging technologies help me to contribute writings about current trends and highlight challenges. I try to bring up diagrams and infographics along each topic to clarify concepts in a simple way. I like also to raise controversial topics for public discussion and exchange of knowledge. I welcome all comments.
Mohammad Amer Shallah, Auto-ID Support, www.ai-support.com
Terms of Use and Copyrights: https://goo.gl/Rl5XoS
---
Other Barcode news of interest:
- OnContact CRM 10 Moves the CRM Market Forward
- Scanco Software Recognized as a 2017 Top 25 Logistics Technology Solution Provider
- Resilinc Named Great Supply Chain Partner by SupplyChainBrain
- ScanForce WMS and Bar Coding for Sage 100 Added to Top-Sage-Resellers.com
- Global Chipless RFID Market 2017-2021: Key Driver in the Market
- Code Collaborates with Wayne Fueling Systems for Validation with Point of Sale System
- Profit Leaks Plague Distribution Sector According to The MPI Group
